While artificial intelligence, or AI, has only become mainstream thanks to the exploits of OpenAI, the company behind ChatGPT, DALL-E, and more, has always existed. For instance, it is responsible for finding answers when you ask a smart assistant such as Siri or Alexa a question. Moreover, AI lets you unlock your phone when you place it in front of your face. It has also driven research into driverless cars. And if you are an avid gamer who uses the latest generation GPUs, you are likely to have used AI-driven technology. Nvidia’s Deep Learning Super Sampling (DLSS) technology, for instance, uses AI to generate additional higher-resolution frames, enabling users to enjoy better resolution and more frames per second (FPS) from a lower-resolution input.
Perhaps less recognized – compared to the likes of ChatGPT – is how AI is used in the CAD industry. As tech companies – small, mid-market, and large – have been hard at work developing AI-driven solutions for their target consumers, so too have developers like PTC Inc., Autodesk, Siemens Digital Industries Software, Nemetschek Group (parent company of Graphisoft and Vectorworks), and Dassault Systèmes. It is thanks to the efforts of the latter group of companies that we now look at the role of artificial intelligence in the CAD industry.
Table of Contents
Brief Overview of AI in CAD Industry
Intelligent designs are not a new concept. So old is it, in fact, that a 2022 research paper notes that the first proposal of intelligent designs was in the 1960s at the early stage of CAD development. Nonetheless, AI in the CAD industry has only become more prominent in the last few years, thanks to cutting-edge developments in the tech world led by the likes of Nvidia, whose chips power AI data centers.
In the CAD world, like anywhere else, computer systems are trained using data and models to become intelligent. Here, model-based reasoning (MBR) merges CAD with AI. The systems use qualitative and quantitative analysis to predict what should exist next or between various parts of a design.
The training data often includes design data and documentation from completed projects as well as real-time software usage by veteran users. Upon synthesizing this data, the systems can now utilize the knowledge to come up with intelligent suggestions that designers and engineers can use to guide their decision making. The systems can also identify patterns in data from different sources, offering better and more profound insights or bettering design practices.
AI-Powered CAD Design and Modeling
Developers of CAD software are increasingly acknowledging the power of AI in eliminating repetitive tasks, improving productivity, and providing intelligent and helpful suggestions. As a result, they are increasingly integrating AI-driven solutions into their products.
For instance, software products now use AI algorithms to generate multiple permutations of designs based on user-defined objectives. They then parade the permutations within a single user interface, enabling the user to evaluate them visually. Additionally, some products feature evaluation metrics that simplify the comparison process. This is known as generative design, and it uses automation to provide better insights regarding a design, thus enabling faster and better decision making.
Thanks to AI, repetitive tasks, such as selecting similar components, can be automated. AI can even offer suggestions that improve the workflow, resulting in better productivity. Additionally, the AI-driven speed-recognition capabilities eliminate the need to manually select frequently used commands. As if that’s not enough, some software solutions can be trained to recognize new commands beyond what they had initially been programmed to accept.
Companies and Software Using AI for Design and Modeling
1. Autodesk with Revit
The Generative Design tool in Autodesk Revit produces multiple design options based on your goals (such as maximizing or minimizing the total cost, value per year, or volume outside zoning), constraints, and inputs. It then allows you to evaluate each design against the project objectives. If you did not get it right on the first try, Revit’s Generative Design feature allows you to tweak various aspects of the inputs and goals to generate additional design options. This way, the software enables you to find the best solution possible.
2. PTC with Creo
Creo offers AI-driven generative design to help you deliver only the best designs in less time. The tool generates several optimal designs for a particular engineering problem based on an array of user-defined design requirements. It mandates you, the user, to specify your goals and requirements, including your preferred manufacturing processes and materials. Thereafter, the software generates the best manufacture-ready design. The tool enables engineers to create superior designs and drive quick and efficient product innovation. It also improves productivity and delivers designs that will result in high-quality, lower-cost, and manufacturable solutions.
3. Siemens Digital Industries Software with Siemens NX
Siemens NX is a comprehensive mechanical engineering software package. It leverages AI and machine learning in three primary ways: personalization, smart human interactions, and intelligent suggestions. Importantly, it does this without explicitly programming these characteristics or rules therein. The smart interactions are in the form of predictions – the software uses AI to quickly identify geometrically similar components. Additionally, the software supports voice commands, enabling users to use speech to invoke commands, teach the system phrases or words that enable it to carry out everyday tasks, and navigate menus and operations.
Regarding personalization, NX monitors how a user uses the software to solve a problem, collects this data, uncovers the underlying patterns, and subsequently personalizes the problem-solving experience. More specifically, the software determines the commands that the user uses and their preferred location on the user interface. It then only serves these contextual commands, thus boosting productivity. Moreover, NX learns the efficient workflow of experienced users when they complete a task and uses that knowledge to teach/train new users on how to complete it.
4. Dassault Systèmes with SolidWorks
SolidWorks’ 3D Creator and 3D Sculptor enable users to enjoy the power of AI and ML through the Design Assistant tool. Designed to reduce the number of repetitive tasks, this tool is equipped with a number of AI-driven solutions. These include:
- Selection Helper: it identifies components such as chamfers, fillets, or edges that are similar or symmetrical to what you had picked. It uses AI to predict the components you are likely to select based on what you have done so far
- Mate Helper: It enables you to automatically add or insert additional instances of duplicate objects or components, such as bolts and fasteners. It does this by suggesting locations where such components can fit.
- Sketch Helper: It predicts what you will sketch next based on your earlier sketches. It also quickly creates a duplicate of your earlier sketches. Moreover, it can add these sketches to multiple locations provided they have similar characteristics and features as the geometry surrounding or underlying the first sketch.
- Smart Mate: It automatically creates mates whenever you drag and hold a component in a position where you want it to mate with the surrounding components. This solution automatically recognizes the correct mating faces, enabling it to create fully constrained mates.
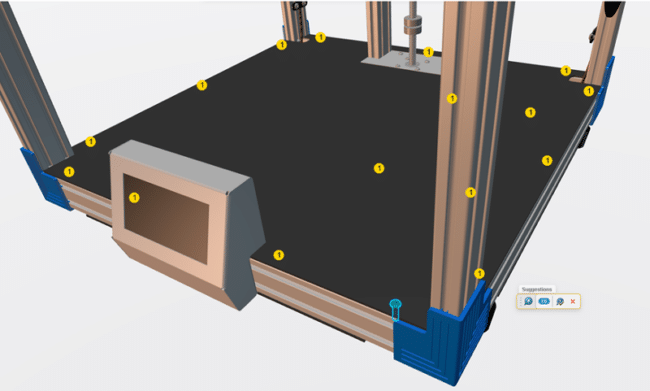
AI-Powered Mate Helper Feature in SolidWorks (source)
SolidWorks has another trick up its sleeves: these tools learn from your workflows, adapting in real time. To put it simply, SolidWorks’ AI algorithms use the data generated as you use the software to gain more insights about your preferences and become even more intelligent.
AI-Powered CAD Analysis and Simulation
CAD analysis and simulation utilizes a number of techniques, ranging from finite element analysis (FEA) and finite volume methods (FVMs) to finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) and dynamic visualization. These techniques have been developed over more than five decades to increase solver efficiency and user-friendliness. Still, challenges remain, with simulations requiring a number of simultaneous trade-offs that revolve around the accuracy and speed of results and the robustness and ease of use of the workflow.
Take the example of FEA. In order to perform an accurate simulation using this technique, the software must prepare the geometry of a 3D model and subsequently create nodes that represent the shape of the geometry. It is the collection of these nodes that is known as a mesh. However, geometry preparation and meshing are considered two of the most time-consuming, expertise-extensive, and error-prone tasks performed in a conventional simulation. How so?
If the meshes are coarse – a situation whereby the nodes are sparsely distributed – the result will be a loss of accuracy even though the simulation will be completed faster. The inverse is also true. Similarly, an easy-to-use workflow with simple meshes will lower the accuracy and trigger other issues.
In such a case, AI can be used to solve these problems. It can, for instance, improve the accuracy and speed of results while ensuring the workflow is robust and easy to use. This way, AI-powered CAD analysis and simulation solutions can boost productivity and help narrow the gap between the ideal world and what happens in reality.
Companies and Software Using AI for Analysis and Simulations
1. Altria with SimSolid
AI-driven analysis and simulation solutions exist. For instance, Altria SimSolid®, a structural analysis tool, enables quick design iterations by generating simulations without meshing and geometry preparation. This way, it reduces the time taken to perform analyses and simulations. SimSolid generally uses a meshless approach to calculating stresses and deflections. More specifically, it utilizes AI and machine learning algorithms to analyze the geometry of a 3D model. It relies on training data that comprises past simulations of numerous models to come up with accurate measures of deflections and stresses.
AI-Powered CAD Building Information Modeling (BIM)
AI-powered BIM solutions aid in intelligent project management. They also enhance safety and mitigate risks. Below are some examples of how BIM solutions have implemented AI.
Companies and Software Using AI for Building Information Modeling
1. Bricsys with BricsCAD BIM
Bricsys utilizes the power of AI and ML in some of its products. Its BricsCAD BIM software, for example, uses AI and ML algorithms to automatically classify building objects or elements. This solution is available via the software’s BIMIFY tool. It allows you to conceptualize and create any shape or object without stipulating the classification. Once you complete the demanding design phase, you can use BIMIFY to add this metadata on your behalf. And while it does this automatically, the software gives you the ability to manually change the classification.
Other BricsCAD AI-driven tools include:
- BricsCAD BIM’s generative design functionality automatically converts a set of solid objects into a building
- Its style guide uses AI to identify a model’s elements and styles and copy it into another project
- The Propagate tool allows you to copy detailed and complex connections between walls and floor slabs, for example, to a similar location on a model
2. Autodesk with Construction IQ
Autodesk Construction IQ is a BIM solution that enables project teams to mitigate risk and improve day-to-day performance. It uses construction language analysis, an AI method, alongside algorithms to understand and predict complex project issues and automatically assigns priority to the most pressing ones. It also learns from the descriptions that quality managers across projects use and subsequently generates issue-specific descriptions.
Moreover, it calculates the risk associated with the issue. What’s more, Construction IQ considers a number of factors surrounding the party responsible for fixing the issue. For instance, it takes into account their past behavior of issue management and current workload, as well as the importance of the issues for which they are responsible. The solution also scans all safety issues on a job site and identifies those that could cause potential fatality. It then brings that knowledge to the attention of safety managers.
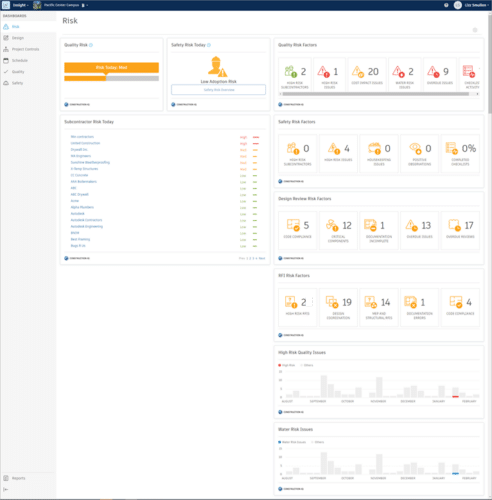
Construction IQ’s AI-Powered Risk Management Tab (source)
AI-Powered CAD Manufacturing
AI in CAD manufacturing can be a boon for manufacturers. Firstly, it boosts productivity by enabling designers and engineers in both senior and junior positions to produce quality designs within a short time. For instance, generative design tools produce an array of designs that have been intelligently created to conform to user-defined goals and requirements. Such designs take into account the manufacturing method as well as the materials to be used. To put it simply, AI-powered CAD manufacturing tools create designs that are optimized for particular goals. Additionally, these designs result in lighter, less expensive, stronger, and more efficient products than those designed using traditional approaches, particularly because the designs are tailored to your preferred manufacturing method.
Additionally, some developers offer AI-reliant tools that monitor the entire manufacturing process. These solutions can predict failure by leveraging an extensive data set that contains parameters associated with certain incidents. Using the power of AI, such solutions can establish when parts will likely fail, the reason for failure, and the exact parts that will fail. Armed with this knowledge, manufacturers can schedule maintenance, preventing unexpected downtime. This way, the solutions optimize the manufacturing process.
Companies and Software Using AI for CAD Manufacturing
1. Autodesk with Fusion 360
Autodesk’s Fusion 360 uses AI to accelerate the entire design to manufacture pipeline through what the developer refers to as generative design in Fusion 360. This tool generates multiple CAD-ready solutions based on manufacturing constraints (such as manufacturing method used), costs, and product performance requirements.
For the software to generate a design, it requires you, as the user, to stipulate the essential geometrical aspects of a problem. For instance, you can select regions that must remain, the load that the part must withstand, and the areas that should be avoided. You should also enter your preferred material options and objectives (e.g., a prompt to achieve a specific factor of safety and maximize stiffness). Once the software generates the designs, it allows you to compare them based on properties that are important to you.
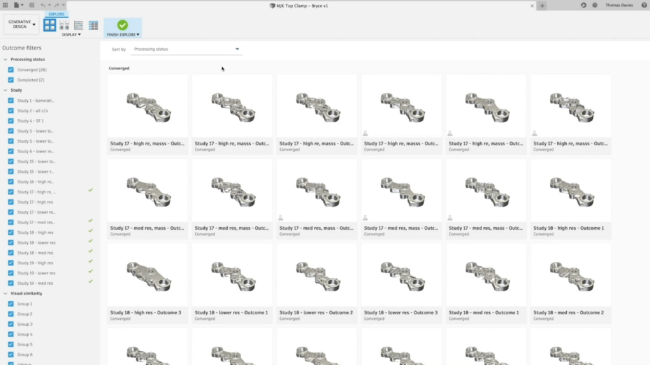
Generative Designs in Fusion 360 (source)
Fusion 360’s generative design in manufacturing offers the following domain-specific benefits:
- CNC machining: It improves consistency across a variety of CNC machines, including 2.5-axis, 3-axis, and 5-axis machines
- Injection molding: It optimizes the effectiveness of high-volume injection molding, achieving higher production rates with lower cycle times
- Casting: It enables the casting of complex shapes, intricate sections, and products with greater mechanical properties; it also reduces the production costs
- Additive manufacturing: It reduces material and time waste and results in better quality time by enhancing innovation and improving design freedom
2. PTC with ThingWorx
PTC Inc. offers an AI-powered industrial internet of things (IIoT) solutions platform called ThingWorx. Among the solutions that form part of this platform is a predictive maintenance tool that uses AI to detect failure by identifying parameters that could cause incidents and predict parts that will fail, why they will fail, and when they will fail. This way, it prevents downtime and optimizes service calls. Moreover, ThingWorx utilizes AI to enable manufacturers to improve overall manufacturing efficiency, optimize production by augmenting equipment effectiveness, and perform remote asset monitoring.
AI-Powered CAD Data Management
Indeed, data management can be laborious, as it involves everything from collection, cleaning, integration, organization, labeling, and cataloging. But AI-driven solutions are increasingly being applied to deal with some of these labor-intensive tasks. In fact, AI has been shown to increase the quality, security, and accessibility of data. For instance, AI can classify data from different sources, including documents, designs, process plans, and more. Furthermore, it can catalog this data, helping users to locate it much faster. Finally, AI reduces errors by handling classification, data collection, structuring, and cataloging.
1. PTC with ThingWorx Navigate
ThingWorx Navigate gives quick and easy access to product lifecycle management (PLM) data such as documents, process plans, drawings, and change requests and notices. It provides ready access to such data via a simple interface, helping users spend less time searching for data.
AI and the Future of the CAD Industry
Increased Adoption of AI in CAD Industry
The future of AI in the CAD industry looks bright, with companies hinting at new AI-driven products. For instance, Ansys, a software company that has created the Ansys engineering simulation software, is currently exploring how it can use AI to improve the accuracy and speed of simulations while making the associated workflow both robust and easy to use.
Similarly, in a late 2022 interview, Graphisoft CEO Huw Roberts hinted at initiatives that will leverage AI. As a subsidiary of Nemetschek Group, Graphisoft is exploring whether to use AI natively on its ArchiCAD software or connect the software to APIs, enabling it to harness the power of AI through the cloud.
But while Graphisoft and Ansys have yet to provide concrete timelines, Dassault Systèmes has, and its prospects are nothing short of exciting. Starting July 1, 2023, according to a presentation by Board Chair and CEO Bernard Charlès during the 3DExperience World 2023 convention, users will enjoy even more AI-powered capabilities on the company’s 3DExperience platform.
For instance, the updated platform will boast better generative designs. It will automatically regenerate the specs of designs created using CAD software and recreate the best possible design, enabling users to reassess and elevate the quality of a design. It will also regenerate designs from scans, with the regenerated design featuring specs that are as close to the scans’ as possible. In this regard, it will save time as it will not require users to manually create the designs. More details will, of course, be made available as the launch nears.
Indeed, these solutions are bound to make AI more available, with the associated impacts being undeniably widespread in the future. For instance, more designers and engineers will get to enjoy more productivity and efficiency, reduced costs and errors, better and more efficient designs, and more optimized manufacturing processes.
Challenges, Risks, and Concerns
But as AI becomes even more widespread, so too are concerns around the following:
- Ethics: AI models have to be trained using data. However, the source of that data may pose ethical questions. For instance, is the data sourced appropriately from the copyright owners?
- Algorithmic bias: AI is only as good as the training data used. Thus, if that data is biased, the AI-driven solution will also have some bias. In the context of CAD, it can lead to the generation of designs that only favor certain conditions while ignoring others.
- Privacy concerns: AI computer systems collect and process huge volumes of data. As such, there is always a risk that the data might be mishandled due to a data breach or intentional data leaks. What happens then when the data leak includes designs of sensitive projects or those that constitute trade secrets?
- Misuse: AI empowers even less experienced CAD users to create robust designs. If such solutions land in the hands of individuals with malicious intent, they can develop products that cause harm.
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence plays a crucial role in the CAD space. It is used to generate designs, improve the quality and speed of simulations, mitigate risks, promote safety, and optimize manufacturing processes. Moving forward, CAD developers are likely to integrate AI into more of their solutions, making the technology available to more users. At the same time, however, it is important to be mindful that AI is not always positive. It has inherent risks and challenges. These include ethical questions, privacy concerns, risk of misuse, and bias.

