Finding the right CAD program for your needs is a tricky endeavor. With the constantly advancing nature of the AEC industry, the software dedicated to helping produce technical drawings grows with it. What we get with that is a veritable smorgasbord of software options. It gets a little daunting to pick between all of these available programs regardless of your experience level.
For regular readers of our blogs here at Scan2CAD, comparison blogs are a familiar thing. We’ve covered program comparisons between Draftsight, CATIA, Solidworks, and various Autodesk products. We take a look at the differences and the similarities between these pieces of software and figure out what kind of CAD work goes well with each of them. Our aim with all of these articles is to make it easier for CAD users to choose the right program for them.
If you’ve clicked on the link to this blog, it might be safe to assume that you’ve at least narrowed your choices to one of two programs – AutoCAD and Fusion360. Today we’ll be looking at both programs individually and then figure out what they have in common as well as how they differ from one another.

AutoCAD and Fusion 360 are only two of many Autodesk programs Source
Table of Contents
AutoCAD
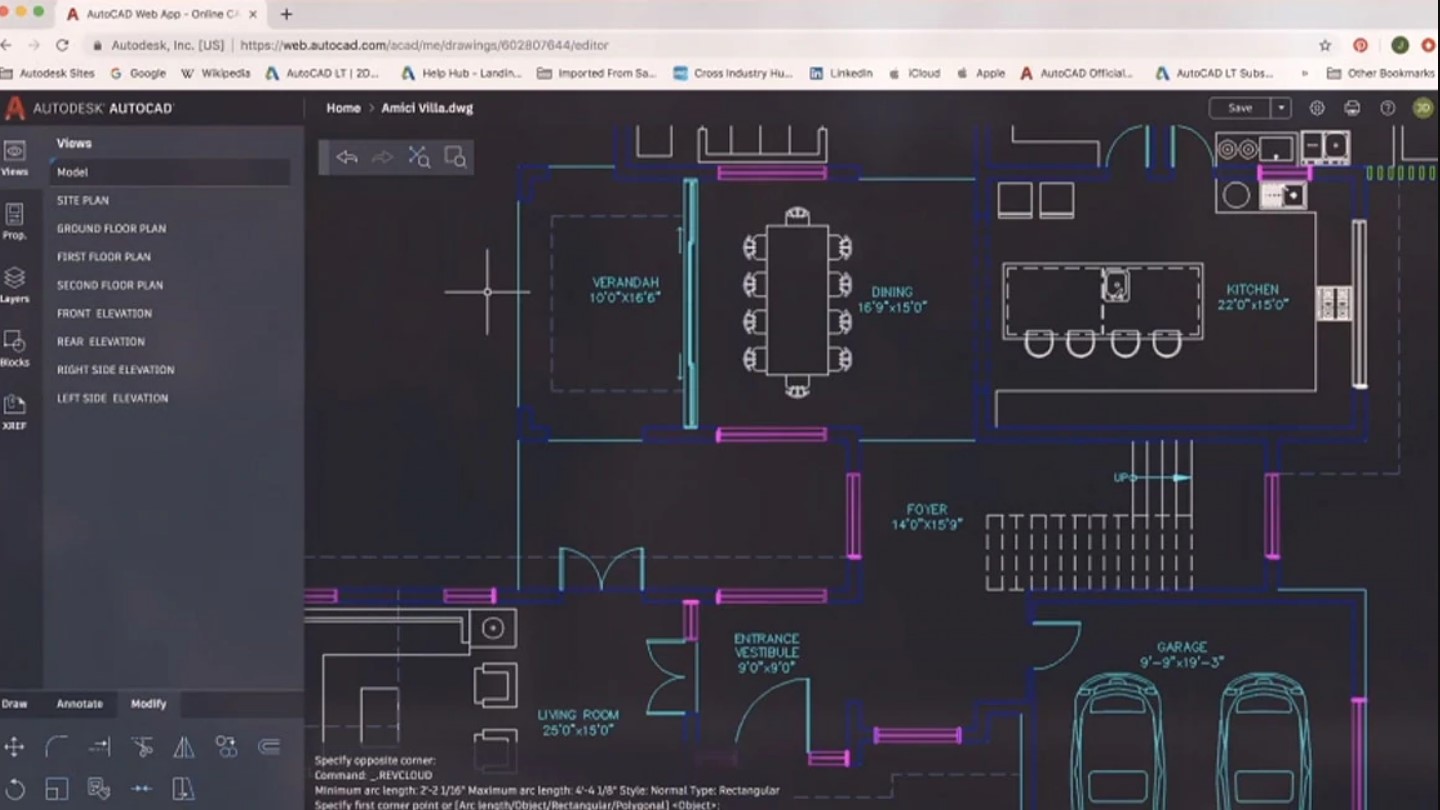
AutoCAD interface Source
History
AutoCAD is Autodesk’s flagship product and is also the first CAD program ever developed for PCs that became so ubiquitously used worldwide. From its conception in 1982 to today, its core function hasn’t changed much – to produce high-quality technical drawings in 2D and in 3D.
Initially, AutoCAD was designed for mechanical engineering and manufacturing professionals. As it proved to be a quintessential boon to drafters, Autodesk has expanded its demographic range to include architects, various other engineers, and construction professionals. Even video game developers, animators, and hobbyists rely on AutoCAD.
AutoCAD is considered to be the foremost CAD program in the AEC fields. You’ll be hard-pressed to find anyone in the industry who isn’t at least familiar with AutoCAD.
What it does
AutoCAD is computer-aided design software – or CAD – that helps professionals in the AEC and manufacturing industries produce both 2D and 3D technical drawings and models. As the program became the standard for CAD, what AutoCAD does in essence is to digitize the drafting process.
Users can conceptualize, draft, and make detailed annotations on 2D vector geometry, 3D solids and surfaces, and edit mesh objects with AutoCAD. AutoCAD users can also do higher-level drafting work such as detailed comparisons of different drawing files or versions of the same drawing file, the creation of repeatable and editable blocks, as well as the production of drawing schedules. And to take it a step further, there are various add-ons that you could install to help automate or streamline any niche tasks you have in your drafting workflow.
More recent versions of AutoCAD have included mobile and web app options, as well as the option to save files onto the cloud. This makes it possible to access AutoCAD files from almost any device and is perfect for any CAD professional who is constantly on the go.
The developers have created specialized toolsets that are industry-specific and make it easier for their target market to use their particular version of AutoCAD to its fullest potential. Here are some of their featured toolsets:
– Architecture: This toolset adds specialized automation tools for the efficient production of architectural drawings, documentation, and schedules. This is perfect for architects and architectural professionals.
– Electrical: Features included in this toolset are the streamlined creation of schematic diagrams and a library of standard electrical symbols. This is mainly geared towards electrical engineers and professionals.
– Mechanical: This is similar to the electrical toolset but has features that include mechanical parts and components. As the name implies, mechanical engineers will benefit most from this
– MEP: This is a bit of a mix of the architectural, electrical, and mechanical toolsets with added functionality for plumbing systems. This is mainly geared towards the design and management of building systems.
– Map 3D: With this toolset, AutoCAD users can seamlessly read and edit GIS topology for the purposes of design and planning as well as geo-data management.
– Plant 3D: More geared towards the manufacturing industry, this toolset helps users create drawings and schematics for plant design.
– Raster Design: The main use of this toolset is to convert raster images into DWG objects. This is similar to what Scan2CAD is able to do, albeit not as robust since it can only produce AutoCAD-specific DWG objects.
Fusion 360
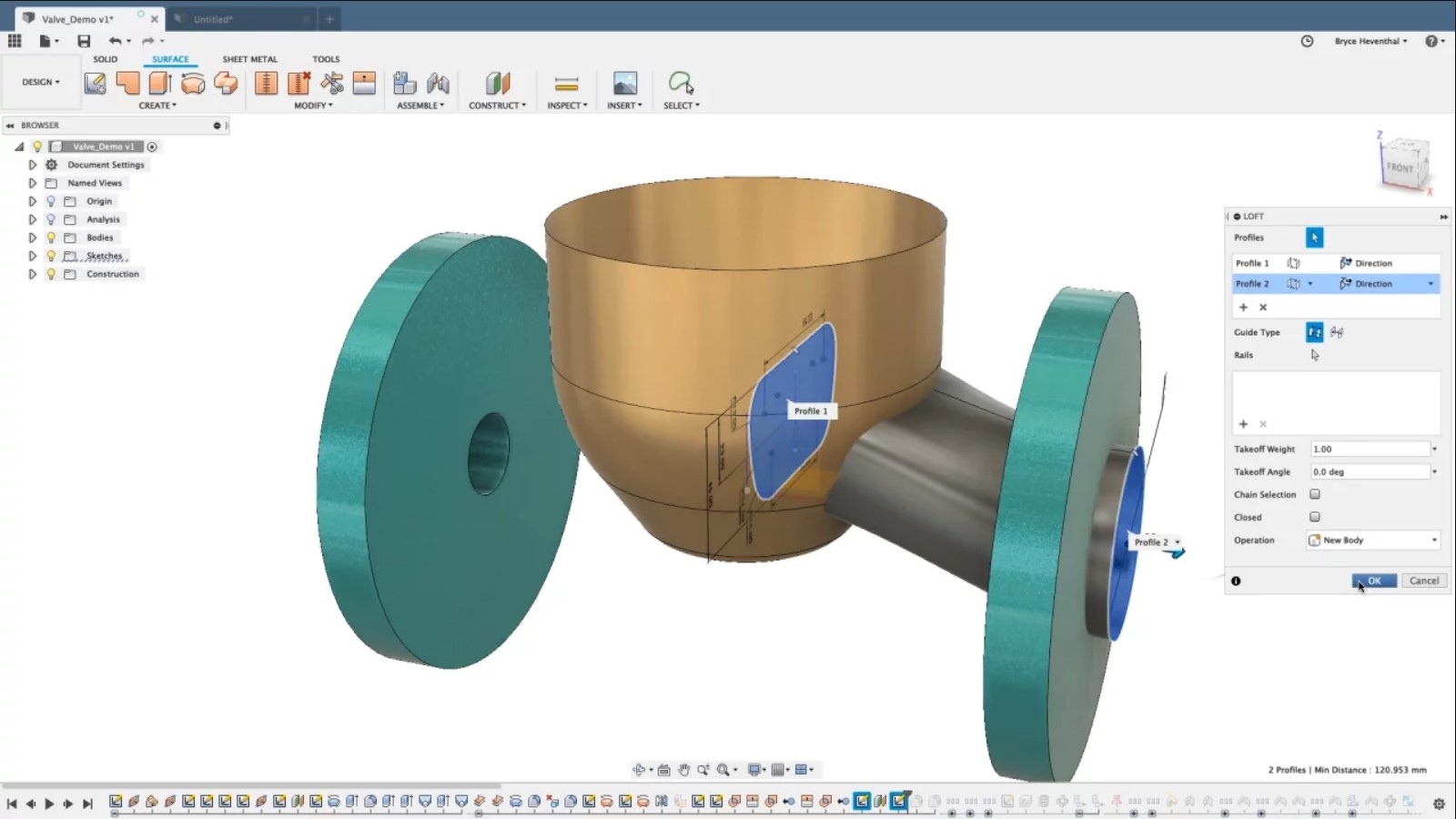
Fusion 360 interface Source
Fusion 360 – another well-known Autodesk product – was released back in 2012 when Autodesk decided to get into the cloud-based software bandwagon although its journey started way before then. On February 4, 2009, Autodesk developed its then newest program, Inventor Fusion. This program was then integrated into already existing programs in 2011. Because of this, Autodesk would then release a program later that year that focused on product lifecycle management – PLM 360. Moving that a step forward, the company then created software that could run simulation testing on the cloud called Simulation 360. Taking in and combining all of the software integrations and developments that it’s been through in the past three years, Autodesk finally launched the final Fusion 360 program in November 2012.
What it does
Fusion 360 is Autodesk’s primary cloud-based CAD program for the AEC and product manufacturing industries. Its various functionalities include the following: 3D modeling, simulation and renders, and accurate simulation and data management. Being a cloud-based program, it also does well with collaboration and documentation.
Fusion 360 is also exceptional when it comes to preparing models for 3D printing, machining, and prototyping.
The main users will find Fusion 360 useful with the following functionalities:
– 3D design and modeling: The program can handle surface modeling, mesh modeling, parametric modeling all other of the major modeling standards. Users will be able to work with independent components or with assemblies depending on the complexity of the project.
– Electronics: This is where Fusion 360 is said to shine – the program can handle different tools for the design and manufacture of printed circuit boards.
– Simulation: Fusion 360’s simulation features include nonlinear stress, modal frequency, buckling, and static stress.
– Visualization: If photo-realistic renders are what you’re looking for, Fusion 360 has you covered in that department. It can also handle details 2D drafts and documents.
– Collaboration: Due to its cloud-based nature, Fusion 360 makes it easy for teams of different people to collaborate and share their work real-time. This makes for a fast and easy way to reach project deadlines.
– Data management: Fusion 360 makes it easy to handle data and metadata about projects and their corresponding files. Not to mention, all the data about your files are securely kept in the cloud.
– Manufacturing and machining: With all its tools, Fusion 360 is great for aspiring 3D printers and machinists. Any model made in the program can easily be exported as any of the standard file formats used by CNC machines or 3D printers.
AutoCAD vs. Fusion 360
Here are some clearer differences between AutoCAD and Fusion 360 tabulated:
|
AutoCAD |
Fusion 360 |
|
Is capable of creating detailed 2D and 3D drawings primarily for the AEC industries |
Can create highly detailed 3D models that are useful for CNC and 3D printing |
|
Fewer features but more straight-forward to learn |
More robust functionality but has a steeper learning curve |
|
Best for creating detailed plans and drawings |
Best for product prototyping and simulation |
|
Geometry-driven models |
Freeform models |
|
Primarily works with local and network-based files with options for cloud saving |
Primarily works with cloud technology |
|
Can be operated using the command line |
Does not have command lines |
|
Main users are architecture, engineering, and construction professionals |
Main users are electrical engineering, mechanical engineering, manufacturing, and machining professionals |
Conclusion
In short, if you’re looking for a no-fuss way to produce architectural and engineering drawings and plans, you can’t get much better than AutoCAD. If you’re an engineer or machinist more inclined to using 3D models, simulation tools, and realistic visualization, you’ll want to try out Fusion 360.



