The DWG (or ‘drawing’) file format stores and describes the content of 2D and 3D design data and metadata. When it comes to accuracy, precision and detail in your design drawings, there’s not many better formats than DWG (file extension, .dwg).
A proprietary format developed by Autodesk, a specialized CAD package is required to open a DWG file. Whilst the format was developed for AutoCAD, it can be viewed with a range of CAD programs (including Scan2CAD!) Although first developed in the 1970s, DWG is still a popular file format used by millions of people worldwide. Nowadays, DWG is the preferred native file format for many other CAD applications (like Caddie, IntelliCAD, etc.) and non-native file format for some others.
File Structure
DWG–being a popular format used for a range of design applications–has a robust file structure. The various components of a DWG file are listed in the most recent Open Design Specification (version 5.3) for the format. A typical file structure will include the following:
| Section | Basic description |
| Header | This consists of File Header, DWG Header variables and information about the error detecting algorithm, i.e.the cyclic redundancy check (CRC). Each subsection is a specialized vector where different lengths of bits are used to represent different labels. For instance, the first 6 bits of the DWG Header variable stands for the version string. |
| Class definitions | There are numerous classes, and their inclusion/exclusion depend on the specific .dwg file purpose. The section includes the class metadata size of class data area, class number, and checksum, among others. |
| Template | (Optional) For R14 and R15 users, this section is below the Object Free Space section. |
| Padding | A specific number of bytes before and after the metadata. Padding was required in order for the older AutoCAD software versions to be forward compatible to the new DWG file format. |
| Image Data | For R14 and R15 users, this section is optional and inserted below the Template.The metadata for this section depends on the specific type |
| Object Data | This includes a complete list of table entities, dictionary entries, etc. corresponding to the existing list of objects. |
| Object Map | This section specifies the location of each object in the file. Most of the metadata in this section are file handles that play a role in identification and re-rendering of the object |
| Object Free Space | This section is optional for all users |
| Second Header | A duplicate of the file header section towards the end of the DWG file |
Navigating through a DWG file
Due to the complex nature of the data and metadata contained in DWG files, navigating through them might not be the easiest of things to do. Most of the information contained in the DWG file is at the bit-level. Bits (1 or 0), bit triplets (1 to 3 bits), bitshort (16 bits), and bitlong (24 bits) are the units for which information can be retrieved. Some data is in an encrypted state – they hold valuable information when decrypted.
Downloading DWG file specifications

The complete list of DWG file specifications released by OpenDesign can be downloaded for free.
Features
DWG is a binary file format, which simply means that it is not entirely human-readable like the plain ASCII English text you’re reading right now – the information is read and interpreted byte by byte by a suitable file reader. The binary encoding of DWG files is based on the information provided by the user, and this information can be partial or complete. A DWG file typically includes information about the image coordinates and any metadata associated with it. A DWG file viewer renders an image view in two or three dimensions, based on the vectorised information encoded in the DWG file.
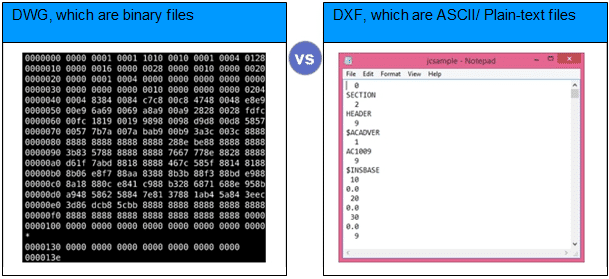
The DWG file format encodes information in 1s and 0s – as opposed to another popular CAD format, DXF, which uses ASCII
The DWG format is a highly specialized vector format to store images in the most precise and systematic manner. Once generated, a DWG file can be immensely useful in rendering the image data for a variety of engineering design purposes.
Got any burning questions about DWG files? Check out our guide to some of the most commonly asked questions about DWGs.

