Earlier this year, Scan2CAD released version 9 – with one of the key updates being support for the DWG file format. DWG is one of the most ubiquitous file formats in the CAD world. It’s the native file format for AutoCAD and is used by CAD professionals in every industry. In this article, we explain the basics of the DWG file.
The DWG file format is used for storing two- and three-dimensional design data in CAD drawings. Did you know that the acronym DWG literally stands for drawing? It is the native file format for AutoCAD data files, or default file format that AutoDesk uses to create and save files. In fact, the .dwg file extension would suggest that the drawing is definitely compatible with AutoCAD software.
The DWG file format was created in 1982 by AutoDesk, way back when they first launched AutoCAD software. It is a proprietary file format, which means that the specifications for DWG is not publicly documented. Third-party application designers would have to purchase a license or API from AutoDesk, so that their software can read and write DWG files. This is unlike the equally popular DXF file format, which is open-sourced and supported by virtually all CAD software.
What kind of information can you store in a DWG file?
The DWG file format stores both vector image data and metadata. The vector data serves as instructions to the CAD application on how to display (or render) the drawing. Meanwhile, the metadata saves information such as author, file data, location data, client data and so on. There is a specification document that defines exactly how different types of information and CAD entities are encoded.
So, what kind of images can be saved as a DWG file?
A DWG file can portray all sorts of images – everything from building specifications to dimensions for mechanical parts, maps to animated walk throughs. Basically any information that a user enters into a CAD program can be stored in a DWG file. A few broad categories:
- Designs. A drawing design is usually made up of elements like lines, polygons and text; all of this is encoded in the DWG file format
- Geometric data
- Maps and geographic information
- Photos
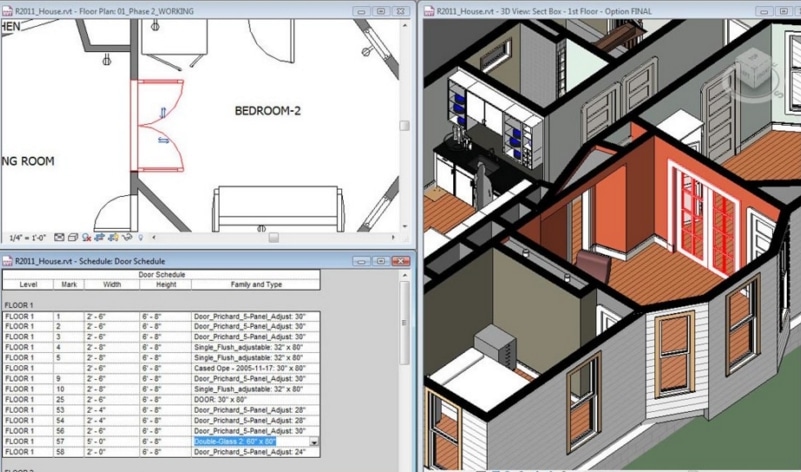
Here’s a drawing of a house, saved as a DWG file. As you can see, the file stores 2D and 3D data, as well as a database of dimensional data.
Who uses DWG files?
DWG files are used by CAD professionals in various industries, including architects, engineers and designers. There are many specialised versions of AutoCAD serving vertical niche markets. There’s AutoCAD Civil 3D that is used for infrastructure modelling, AutoCAD Electrical for designing control systems, AutoCAD Map 3D for geographic information system (GIS) mapping and so on. DWG files are widely used in CNC applications too.
Which CAD programs use DWG files?
AutoCAD, Autodesk DWG TrueView, IntelliCAD CorelCAD, Adobe Illustrator, Scan2CAD; to name a few.
How do I view and edit DWG files?
There are several ways to view and edit DWG files without AutoCAD software. AutoDesk has a few free solutions: A360 Viewer, which is a browser-based file viewer; DWG TrueView and AutoCAD 360, which is a mobile or web app. Of course, you can also view DWG files with other CAD applications that support DWG.
These file viewers come in handy if you’re only viewing CAD designs. Not all of them include the functionality to make annotations to DWG files or to convert them into different file formats. To make edits, you’d need full CAD software packages that support DWG.
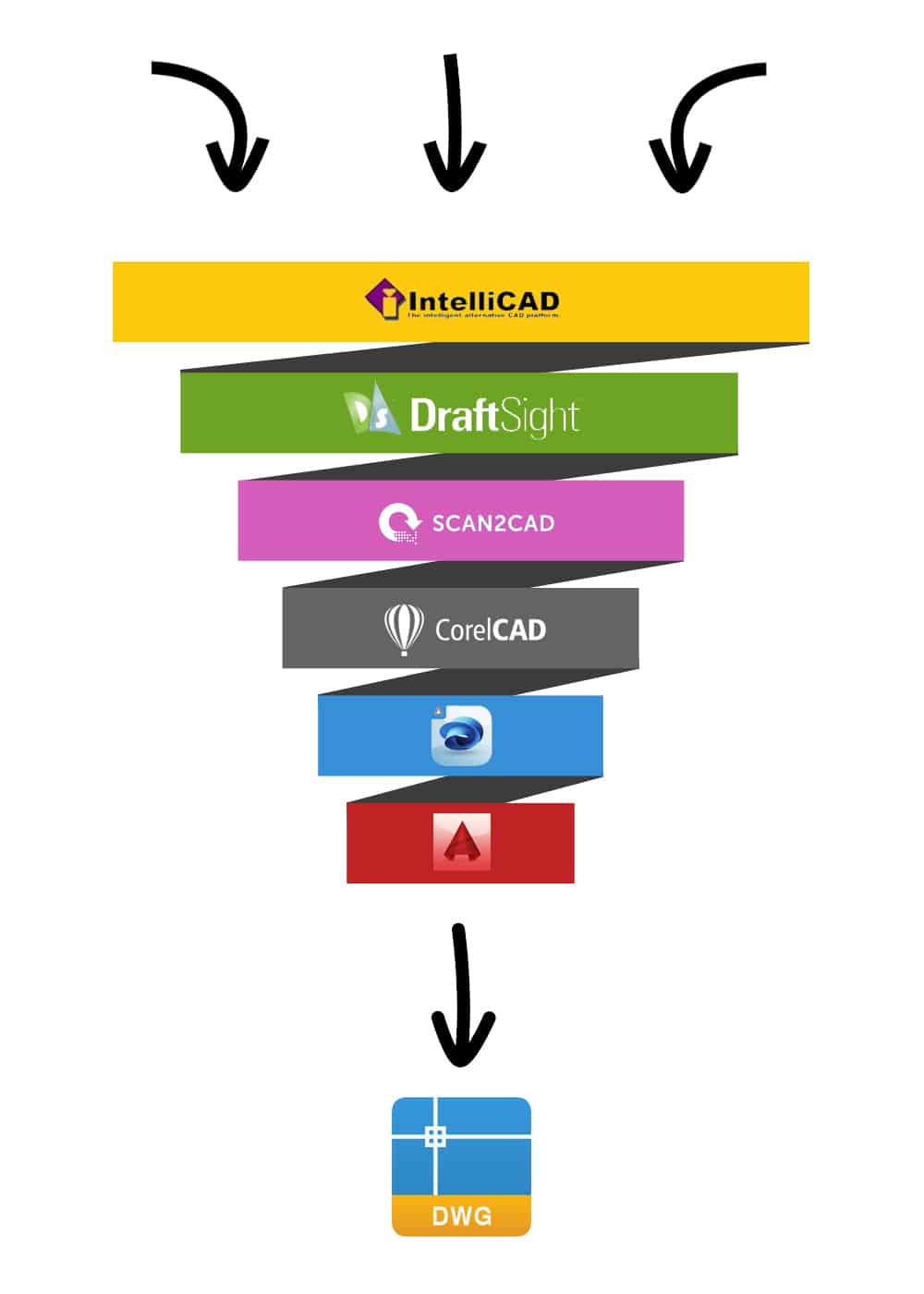
Various CAD software that you can use to view and edit DWG files.
In the coming weeks, we’ll be publishing a full set of guide articles to the DWG file format. We’ll dive into how different industries use the DWG file format, how to view and edit DWG files and most importantly, DWG file conversions.